ワニバサミの使い方とメンテナンス
February 04, 2026
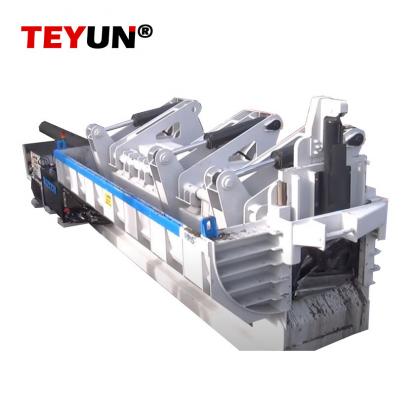
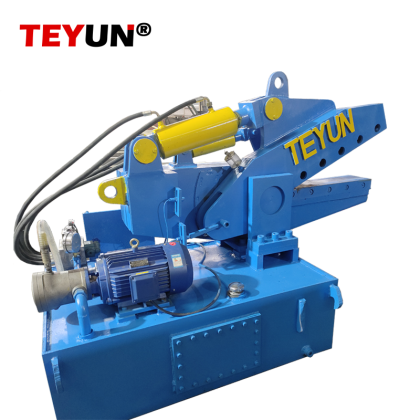
I. アリゲーターシアーの安全操作手順
1. 運転前点検:
個人用保護具: 安全ヘルメット、保護メガネ (フェイスシールド)、耐切創手袋、耐衝撃性と耐穿刺性の安全靴、聴覚保護具、作業服を着用してください。
機器の点検: 油圧オイルのレベル、油圧ラインの漏れ、ブレードの損傷や亀裂、すべての留め具の確実な締め付け、および電気システムの適切な機能を確認します。
作業エリア:作業エリアを清掃し、地面が安定し、障害物がないことを確認してください。作業者以外の人は安全な距離を保ってください。明確な警告標識を設置してください。
2. 操作中の注意事項:
適切な材料供給:切断する材料(鉄筋、構造用鋼、鉄スクラップなど)は、できるだけ刃軸の根元(せん断力が最大となる部分)に近づけて配置してください。切断中に材料が跳ねたり滑ったりしないよう、材料が安定していることを確認してください。
用途範囲外の使用は厳禁です:密閉容器(爆発の危険)、可燃性・爆発性物質、通電中の電線・ケーブル、または過度に厚い鋼板など、用途が明確に定義されていない材料は絶対に切断しないでください。機器に指定された最大せん断能力(直径/厚さ/材質)を必ず遵守してください。
プロセス制御:
せん断を開始するときは、手や体のすべての部分を刃や材料クランプ装置から遠ざけておく必要があります。
長い材料をせん断する場合は、せん断後の揺れによる傷害を防ぐために、補助装置または人員を使用して端部を安定させる必要があります。
材料が詰まった場合は、何らかの処置を行う前に機械を停止し、圧力を解放する必要があります。
集中力を維持し、疲労した状態での操作は避けてください。
3. 手術後:
ブレードを完全に開き、機械を停止します。
刃とその周囲のゴミや不純物を取り除いてください。
機器を安全で水平な場所に駐車してください。
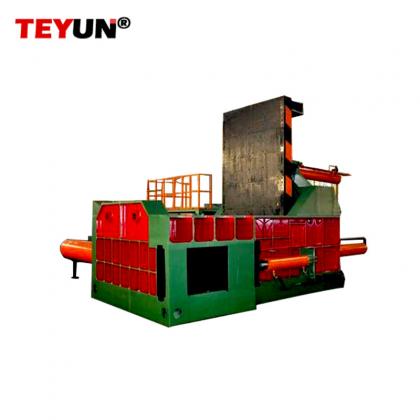
II. ワニ口鋏の日常的なメンテナンスと手入れ
システムメンテナンスを行うことで、機器の寿命を大幅に延ばし、故障を減らすことができます。
1. 日常のメンテナンス:
清掃: 作業後は、機器、特にブレード、シリンダーピストンロッド、センサー領域からほこり、金属の削りくず、油を取り除きます。
検査:
刃の摩耗や欠けを点検します。
すべての油圧ジョイントとパイプラインにオイル漏れがないか点検します。
電気配線に損傷がないか確認してください。
すべての潤滑ポイント(カッター シャフト ピンなど)にグリースが必要かどうかを確認します。


 住所 : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province
住所 : Mingjue Industry Park, Lishui District, Nanjing City, Jiangsu Province

 English
English français
français русский
русский español
español العربية
العربية Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt 中文
中文
















 IPv6ネットワークをサポート
IPv6ネットワークをサポート